What does a cloud data management entail, and why is it vital to so many organizations? Cloud computing consists of many components – including AI – to deliver the greatest data management experience. It is constantly evolving, and with every development, becomes more in demand.
How does Cloud Data Management differ from traditional Data Management Practices?
Traditional data management practices involve the usage of enterprise data that either resides in on-premise applications and systems or that is brought in from external sources. This approach worked well when most or all enterprise data sat within the firewalls of an organization. With the proliferation and prevalence of cloud-based SaaS applications and business models that utilize multitudes of business partners, data dispersal has become the norm. Another significant change that has occurred in the last 10-15 years is the explosion of social media and Internet-of-things (IoT) systems that has exponentially increased the volume and velocity of data available to companies.
In this environment of dispersed data sources, generation of massive quantities of data as well as variety of data, traditional data management practices built on on-premise data architectures have been found woefully inadequate. Cloud data management as a critical component of enterprise data management is now the norm if an organization wants to leverage the power of data analytics for enabling digital transformation, removing friction in supply-and-demand chains as well as enhancing the quality of business decisions made.
With modern cloud data management, organizations gain agility, flexibility and scalability to respond effectively to a rapidly-evolving business landscape. It becomes easy to incorporate changes in business strategy and have underlying IT systems respond effectively. Cloud data management and integration tools from cloud providers like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud as well as data management tool companies like Informatica and Talend make it easy to stitch together data from a multitude of internal and external data sources. New and varied uses of data to enhance business operations as well as quality of decision-making becomes a reality. The promises of data analytics to establish and enhance relative competitive advantage are fulfilled.
Moreso, all this is being achieved without losing the controls necessary to govern enterprise data. As any data management practitioner worth her salt will acknowledge, data governance policies, procedures and tools to ensure data security, integrity and quality are of paramount, indeed strategic, importance. As has been evident from increased attacks on corporate data by hackers, protecting and securing data has become even more critical. As a component of cloud data management, governance tools have also kept pace with the evolving needs of organizations.
An organization does not have to completely move to a cloud data management paradigm. It can still include traditional, on-premise data management practices as part of its overall data architecture. However, while traditional on-premise data management can manage certain workloads, it may not cater well to modern data demands. As can be seen in the graphic below, it can also be quite costly to manage. A way to avoid this predicament is to develop data storage as cloud-native, allowing data to run and be distributed by cloud-based platforms. This combines sources between on-premise and cloud-based management, giving the best of both worlds – on-premise when necessary, but able to travel to the cloud if workloads demand it.
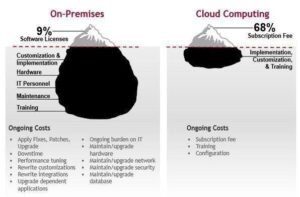
http://www.databax.co.uk/blog/thebest-cloud-computing-infographics-and-images-ever#.Vt06X5MrIUE
Key Components of Cloud Data Management
AI-driven Enhanced Intelligence
Cloud platforms present us with what could be considered one of the most successful and subtle uses of artificial intelligence. Through the scope of AI, we can automatically discover and organize data across all systems, define relationships through certain insights, and perform regular quality tasks that align with policy.
AI is a significant component, as it is now a vital cog to nearly all of the cloud’s other functions.
Data Quality and Governance
The sheer importance of the role data plays in an organization highlights the need for quality. No matter the organization, the data should be reliable and superior. The use of AI is what makes cloud so accurate with its data, often helping organizations reach a new feat in their productivity.
Data governance is responsible for organizing your data– encompassing metrics, customer demand, audience behavior, etc. It ensures the consistency of your data before jumping to analysis and insights. Cloud data management is known for its quality and ease-with this structure it is nearly effortless to access, track, analyze, and use data.
Defensible backup and recovery
A common risk with data is its backup and recovery structure. This is something all organizations can recognize and are constantly seeking to strengthen.
When it comes to the cloud, the most common and beneficial practice is to be cognizant of where your backups are stored and make sure they lay elsewhere from the place your data currently resides. In the event of a data breach, this will help minimize any data loss if not prevent it entirely. Not only is it necessary to backup data, but it is recommended to back up your cloud infrastructure configuration, should you ever require rebuilding. With these two security measures in place, cloud data management can firmly protect your business.
To learn more about Cloud Data Management, Trinus is your go-to to discover cloud-based digital transformations. Contact us today and follow us on all platforms to get the scoop!